
All About Tungsten: How do I know what Tungsten to use?
Aug 25th 2017

Coming in at number 74 on the periodic table, tungsten is an element with a wide range of applications. A rare metal with an extremely high melting point (over 6000 degrees Fahrenheit) and a hardness that surpasses that of most steel, tungsten is used in items ranging from incandescent light bulb filaments, x-ray tubes, radiation shielding, military applications in penetrating projectiles, and of course, TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding.
As most of our readers probably already know, TIG welding is an arc welding process using the combination of a tungsten electrode and an inert shielding gas. The electrode carries the welding current to the arc while the shielding gas (argon or helium) protects the electrode and the welding area from oxidation and contamination. Tungsten is used for its aforementioned hardness and high melting point, and when alloyed with other metals, it can make an electrode more suitable for different projects. Selecting the appropriate electrode for a job comes down to a list of variables, including base material, material thickness, and alternating or direct current.
Naturally, all of these components can become rather confusing, but there is a lot of great information available to help you make the right choice. Included below are a couple of tables outlining the specifics of the more common options available.
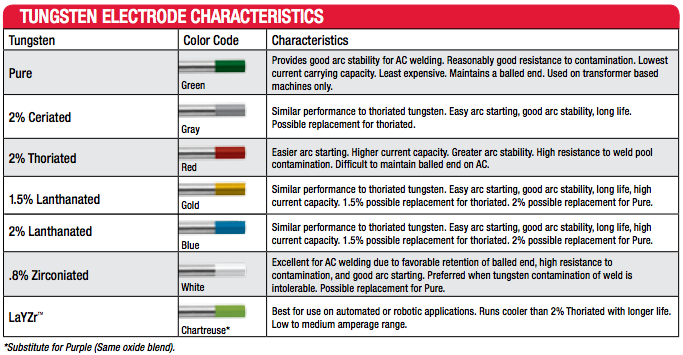
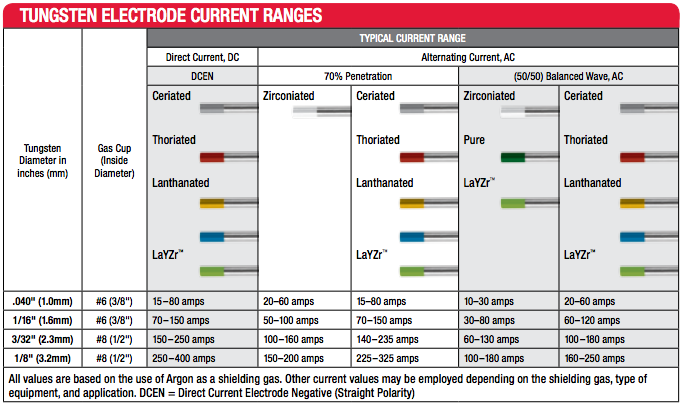
Shop Tungsten electrodes in a variety of sizes, here: weldfabulous.com/welding/filler-metals/tungsten/
As always, when in doubt, do your research, and remember to shop Weldfabulous.com for all your welding needs!
