United Abrasives/SAIT Guide to Choosing the Right Cutting Wheels for Every Application
Mar 30th 2022

Thin cutting wheels have made the job of the welder, fabricator and maintenance technician easier by providing a quick and simple way to cut a piece of metal without the need for other bulky equipment (torches, large saws, etc.).
But all the benefits of a particular wheel don’t mean a thing if it’s the incorrect wheel for the job. United Abrasives/ SAIT offers nine different cutting wheels, all for varying applications because each wheel has its own unique characteristics that allow it to perform well in different situations.

To get started, let’s take a look at what you need to know about cutting wheels before selecting one for your job.
Why use a cutting wheel? The key advantage to using a cutting wheel and angle grinder is that they are easily configured to cut when needed.
Thin .045 cutting wheels are designed specifically for cutting metal. They have a much thinner thickness (known as “Kerf”) than grinding wheels (1/4”) and pipeline wheels (1/8”). This is because grinding and pipeline wheels are mainly designed for grinding metal as opposed to cutting. The added thickness of a grinding wheel makes it difficult for cutting jobs, as the user would need to remove more material in a cut, leading to a longer cutting time and frustration.
Here’s some other facts you need to know about United Abrasives’ cutting wheel catalog:
- United Abrasives .045 wheels are the best choice for efficient cutting. They should never be used for deburring metal after cutting or grinding. This type of misuse could result in wheel failure resulting in severe injury.
- United Abrasives .090 wheels are designed for cutting and notching metal. Notching is the metalworking process of removing material between two cuts to create a slot. This allows for a matching piece of material to be inserted. The fabricator can achieve a tighter tolerance to the joint which allows for easier welding.
- United Abrasives’ most versatile cutting wheel is the Ultimate Combo wheel which has a .095 thickness. This product allows operators to cut, notch, deburr and light grind without the need to change the wheel.
Types of Cutting Wheels
There are two basic configurations of cutting wheels:
- Type 41(1): This is a flat cutting wheel that allows for a maximum depth of cut. The main disadvantage of using a Type 1 wheel is that they mount closer to the guard making it more difficult for the user to see what they are cutting.
- Type 42(27): Originally developed and patented by United Abrasives, this design features more of a rigid feel while cutting, enhanced operator visibility of the cut, and the ability to flush cut as the raised hub allows for the locking nut to be recessed. These wheels are also available with a 5/8-11 quick change hub for ease of mounting.

Grains
The grain used in a cutting wheel determines the wheel’s cutting speed, life and cost ratio.
You’ll find three different types of grains in United Abrasives’ cutting wheels:
- Ceramic - Ceramic grain utilizes the latest technology in abrasives. By design, it features thousands of sharp cutting edges which fracture under relatively light pressure and expose new sharp cutting edges. Ceramic cutting wheels allow for a very long life and fast cutting speeds. Ceramics also tend to cut cooler, minimizing discoloration while maximizing product life. Within the United Abrasives product line, the Saitech™ and The Ultimate Ceramic™ cutting wheels both feature ceramic grain technology.
- Zirconium - Zirconium grain has an extremely durable design. These wheels are used for high performance cutting with long life and feature a low cost-per-cut ratio. Within the United Abrasives product line, the Z-tech™ cutting wheels feature zirconium.
- Aluminum Oxide - Aluminum Oxide is the most common abrasive grain and delivers very good cut rates and durability. It tends to have a lower initial cost for the user which lends to its popularity. Within the United Abrasives product line, the A60S and A46N feature aluminum oxide grain.
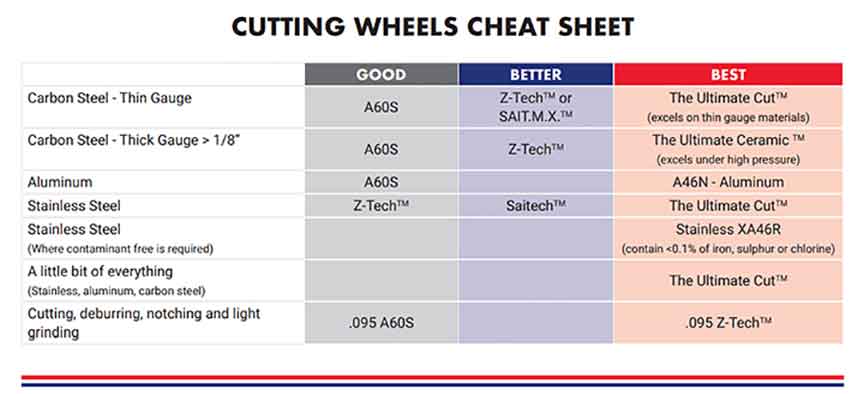
So, which wheel to use? It depends on what you’re cutting and your preferences. Use the chart below to help you determine the appropriate wheel.